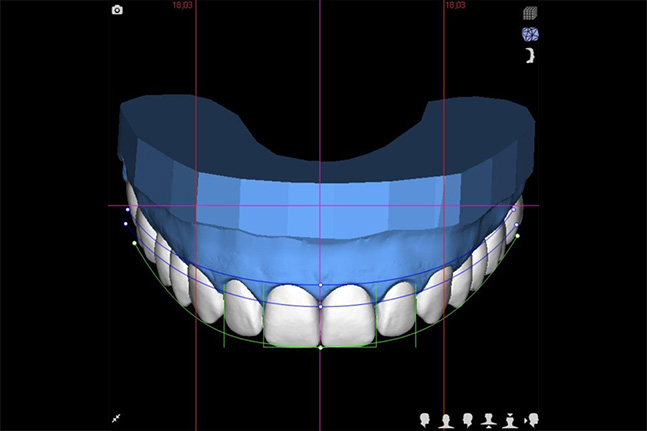
Digital Smile Design (DSD) is a specialised workflow that combines clinical records, digital technology, and laboratory collaboration to help dentists plan functional and aesthetic restorations with precision. At Smile Art Lab, we work exclusively with dental professionals to support predictable treatment outcomes through accurate 3D planning.
Key Takeaways
- DSD is a planning protocol, not a standalone treatment.
- The workflow includes digital records, design approval, mock-up/PMMA test drive, and final ceramics.
- Smile Art Lab partners with dentists only, never directly with patients.
- Focus is on predictability, collaboration, and clinical efficiency.
Understanding Digital Smile Design (DSD) in Practice
For dentists, DSD is more than visualisation; it is a structured planning system. By combining photographic and intraoral data, Smile Art Lab assists clinicians in mapping treatment outcomes before restorative steps are taken.
Key considerations include:
- Tooth proportion and symmetry
- Gingival margins and smile line
- Occlusion and functional stability
- Integration with overall facial aesthetics
Our role ends at planning and design. The dentist completes the restorative phase (veneers, crowns, implants, etc.) with laboratory collaboration.
The DSD Workflow
1. Record Collection
High-quality photos, and intraoral scans form the foundation of the digital plan.
2. 3D Design & Approval
Our team collaborates with the dentist to create a visual proposal. Approval ensures the plan is clinically viable and aligned with patient expectations.
3. Mock-up / PMMA Test Drive
A temporary mock-up or PMMA restoration allows dentists to evaluate function, aesthetics, and phonetics in real conditions before committing to final ceramics.
4. Final Restorations
Once the test drive is validated, the dentist can prep the teeth and we can proceed with the final restoration.
Clinical Considerations
Dentists should evaluate each case by balancing aesthetics and function:
- Occlusion & bite stability – avoiding long-term complications.
- Tooth preservation – planning minimally invasive options.
- Material selection – ensuring durability and shade harmony.
- Periodontal health – confirming a stable foundation before finalisation.
Predictability Through Collaboration
The strength of DSD lies in predictability. With a structured digital plan, dentists reduce errors, improve communication, and achieve consistent results. Smile Art Lab provides the planning support so that restorations can be delivered with confidence.
Records That Drive Precision
The foundation of every DSD case lies in accurate records. Without complete, high-quality inputs, the design cannot be relied upon. Dentists are responsible for collecting and submitting the following:
- Intraoral scans or impressions – Digital scans are preferred for efficiency and detail, but conventional impressions can be digitised when required.
- Extraoral photographs – Full-face and profile shots provide reference for symmetry, smile line, and lip dynamics.
- Video clips (optional) – Short recordings of speech and smiling offer valuable insight into dynamic lip movement and phonetics.
When these records are properly standardised, the laboratory can construct a digital simulation that reflects not just teeth in isolation, but their interaction with the entire facial context.
From Records to 3D Design
Once records are uploaded, Smile Art Lab uses digital platforms to transform the information into a 3D plan. This design process emphasises:
- Aesthetic alignment – Proportions of central incisors, midline position, and gingival contours are digitally mapped.
- Functional evaluation – Occlusion, guidance pathways, and bite stability are tested within the virtual design.
- Treatment feasibility – Designs are reviewed against available space, biological limitations, and restorative requirements.
Dentists receive a draft design that can be reviewed chairside, adjusted collaboratively, and formally approved before any physical stage begins.
The Mock-Up and PMMA Test Drive
An essential step in the workflow is the mock-up, often fabricated in PMMA (polymethyl methacrylate). This temporary stage serves several clinical purposes:
- Verification of aesthetics – Dentists can check whether the proportions, shape, and symmetry match the approved design.
- Functional testing – Phonetics, occlusion, and daily use are evaluated in a real-world setting.
- Patient communication – Although our role is dentist-only, the clinician can use the mock-up as a communication tool to confirm expectations before committing to definitive ceramics.
Adjustments at this stage are far easier and less costly than altering final restorations. The “test drive” ensures the plan is not just digitally attractive but clinically viable.
Transition to Definitive Ceramics
Once the mock-up is validated, the case progresses to the fabrication of definitive restorations. Depending on clinical need, these may include veneers, crowns, or implant-supported units. The key difference is that the design has already been stress-tested digitally and physically, reducing the risk of surprises at delivery.
Smile Art Lab’s role remains focused on accuracy in design transfer, ensuring the definitive ceramics faithfully replicate the approved digital plan. This creates a clear chain of predictability: records → design → mock-up → final outcome.
Practical Advantages for Dentists
- The DSD workflow is not only about aesthetics — It also improves efficiency and risk management. Dentists gain:
- Reduced chairside adjustments – With design pre-tested, fewer modifications are required at delivery.
- Improved interdisciplinary coordination – Orthodontic, periodontal, and restorative plans can be aligned digitally before treatment begins.
- Enhanced patient consent – Dentists have objective visuals to support case presentation and treatment acceptance.
- Documented planning trail – Records of each stage provide medico-legal protection and reference for future treatments.
Integrating DSD Into the Practice Workflow
Adopting DSD requires organisation but quickly integrates into daily practice. Steps to streamline include:
- Standardising record collection – Training team members on photographic protocols and scan accuracy.
- Digital submission systems – Ensuring files are transferred to the lab securely and consistently.
- Clear communication channels – Establishing how feedback and design revisions are shared.
- Scheduling test drives – Allowing sufficient time for PMMA evaluation before scheduling final delivery.
This systematic approach makes DSD less of an “extra service” and more of a core part of restorative planning.
Predictability as the Core Value
Dentists know that unpredictable results erode both efficiency and confidence. The structured DSD pathway counters this by:
- Providing a visual reference at every stage.
- Allowing iterative corrections before finalisation.
- Ensuring that functional parameters are tested, not assumed.
- Ultimately, this predictability leads to improved patient satisfaction, stronger dentist-lab collaboration, and reduced chairside stress.
Case Scenarios Where DSD Adds Value
DSD is especially valuable in:
- Multidisciplinary cases – Where orthodontics, implants, and prosthodontics converge.
- Complex aesthetic rehabilitations – Involving multiple anterior teeth or full-arch planning.
- Cases with altered occlusion – Where changes in vertical dimension or functional pathways must be visualised before intervention.
- Smile line corrections – Ensuring proportional gingival and dental display is balanced to the facial context.
In each of these, the ability to “see before doing” makes outcomes more controlled and defensible.
Continuous Development in Digital Planning
While the principles of DSD remain consistent, digital planning continues to evolve. Advances include:
- Improved 3D integration – Combining CBCT with intraoral scans for restorative-surgical alignment.
- Artificial intelligence tools – Assisting in faster mapping of landmarks and symmetry.
- Cloud-based collaboration – Allowing real-time adjustments between dentist and lab.
Smile Art Lab remains focused not on promoting new gadgets but on ensuring that dentists have access to planning methods that are stable, reliable, and clinically relevant.
Conclusion
Digital Smile Design has become an essential planning framework for modern restorative and aesthetic dentistry. At Smile Art Lab, our role is to support clinicians through precise 3D planning and laboratory coordination, ensuring that each case moves forward with clarity and predictability. Ready to integrate Digital Smile Design into your workflow? Contact us today to discuss how we can support your next case with precision planning and laboratory collaboration.
FAQs
1. What is Smile Art Lab’s role in Digital Smile Design?
We collaborate with dentists to provide 3D planning, mock-ups, and laboratory support throughout the DSD workflow.
2. Do patients contact Smile Art Lab directly?
No. We only work with dental professionals and clinics.
3. Does DSD include the restorations?
DSD is only the planning stage. Restorations (ceramics, veneers, crowns) follow after the design is approved and test-driven.
4. What records are required for DSD?
High-quality photos, and intraoral scans are typically needed to begin the design process.
5. Why use a PMMA/mock-up stage?
It allows dentists to clinically test aesthetics, function, and phonetics before committing to final ceramics.